School of Psychology - Georgia Institute of Technology - Auditory Graphs
One feature of our approach is a focus on relevant technologies. We work with students, educators, and content makers to base our research and development in real challenges in accessible education. We have developed the SQUARE method for grounding our technology in standards such as the Common Core.
The SQUARE method depends on teacher and student help. You can be a part of this process by participating in our research.
The SQUARE method was applied for the development of GNIE software, a graphing system for blind, low vision, and sighted students.
Here are the graphing standards. In some cases, a standard had two separate graphing activities, so the standard was split into two parts.
These standards are based on the Common Core Standards for Mathematics, grade 6. See the Common Core Standards website for more details.
| Standard | Standard Description |
|---|---|
| RP.3 | 1. Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. |
| RP.3.a | 2. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole-number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. |
| NS.6 | 3. Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. |
| 4. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. | |
| NS.6.a | 5. Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself. |
| NS.6.b | 6. Understand signs of numbers in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane; See Results |
| 7. Recognize that when two ordered pairs differ only by signs, the locations of the points are related by reflections across one or both axes. See Results | |
| NS.6.c | 8. Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; |
| 9. Find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. See Results | |
| NS.7.a | 10. Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. |
| NS.7.c | 11. Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation. |
| NS.8 | 12. Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. |
| 13. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. | |
| EE.8 | 14. Write an inequality of the form x>c or x |
| EE.9 | 15. Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. Write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. |
| G.3 | 16. Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. |
Many students can use GNIE to read and write graphs. Here are some examples, organized by standard. These examples were completed by visually impaired students within 7-12 grade.
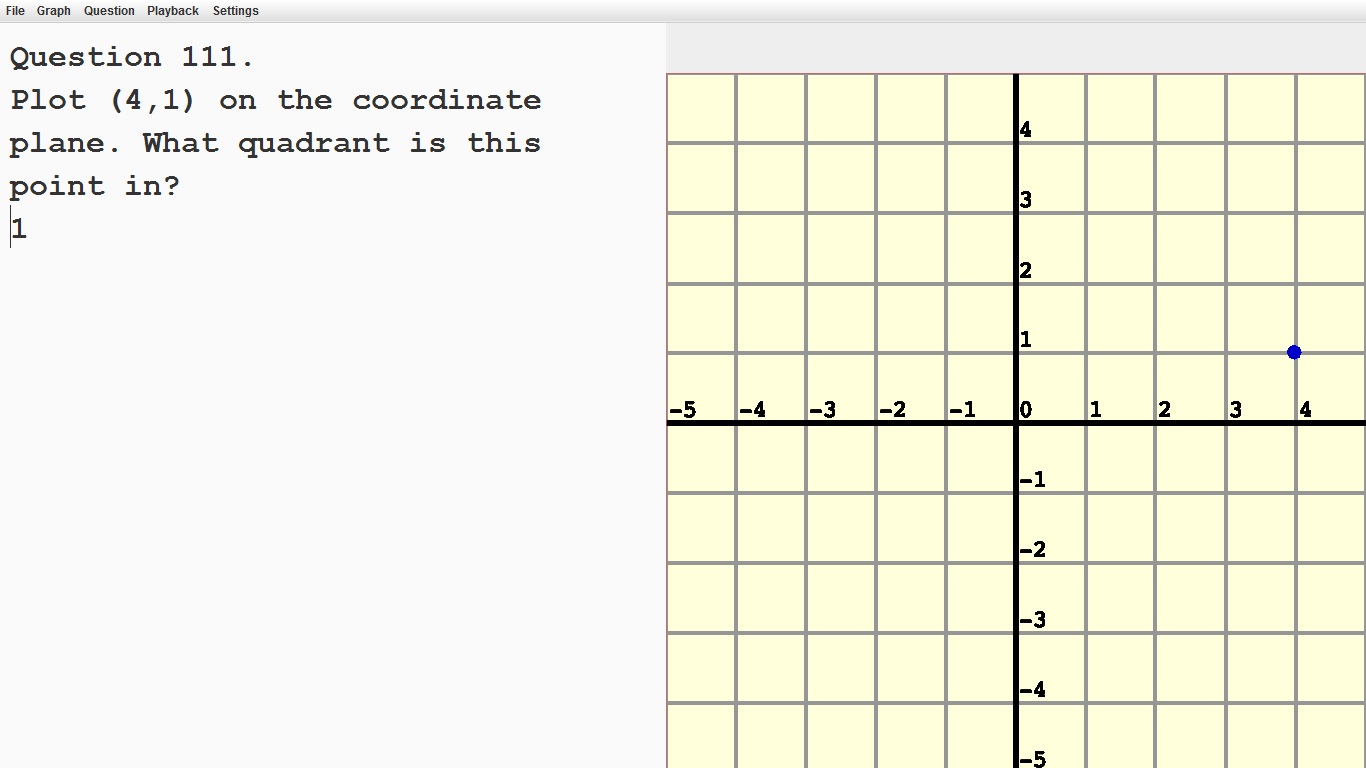
Understand signs of numbers in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants on the coordinate plane.
 |
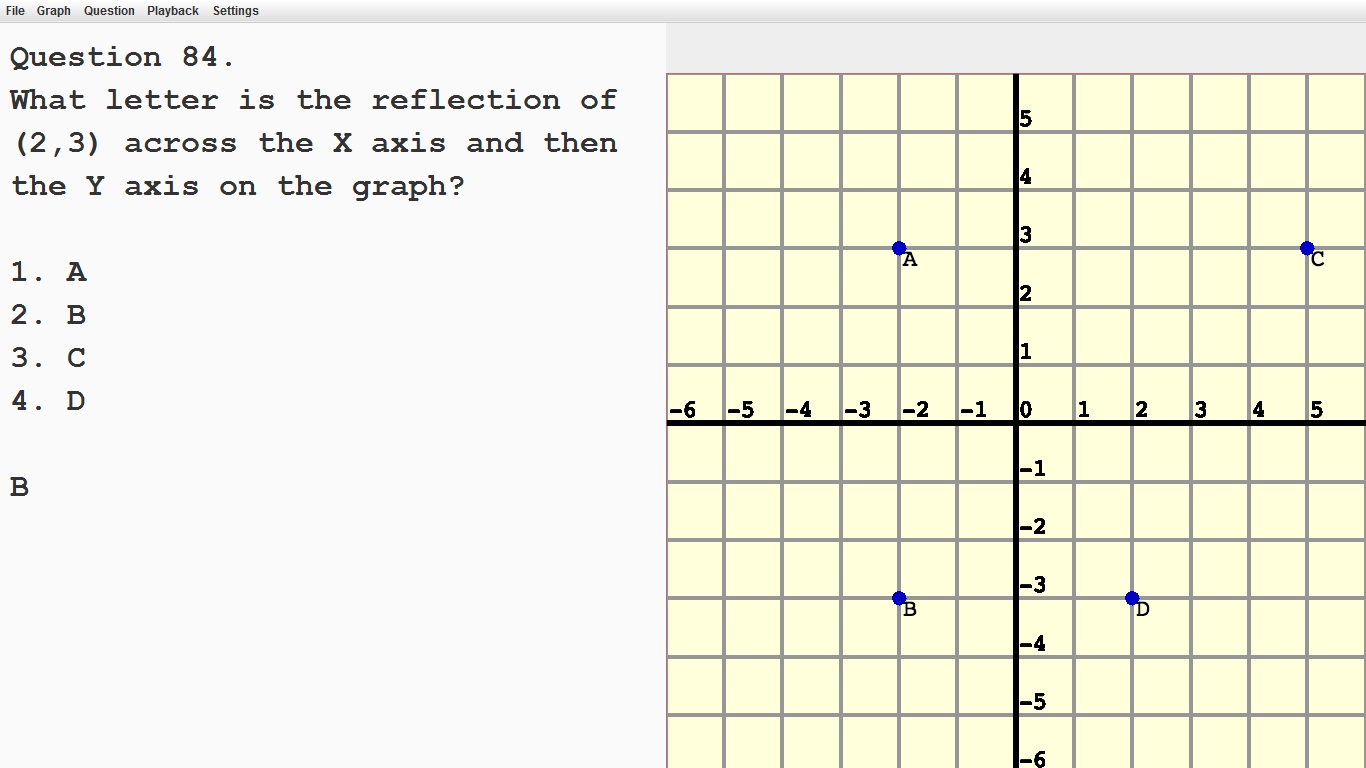
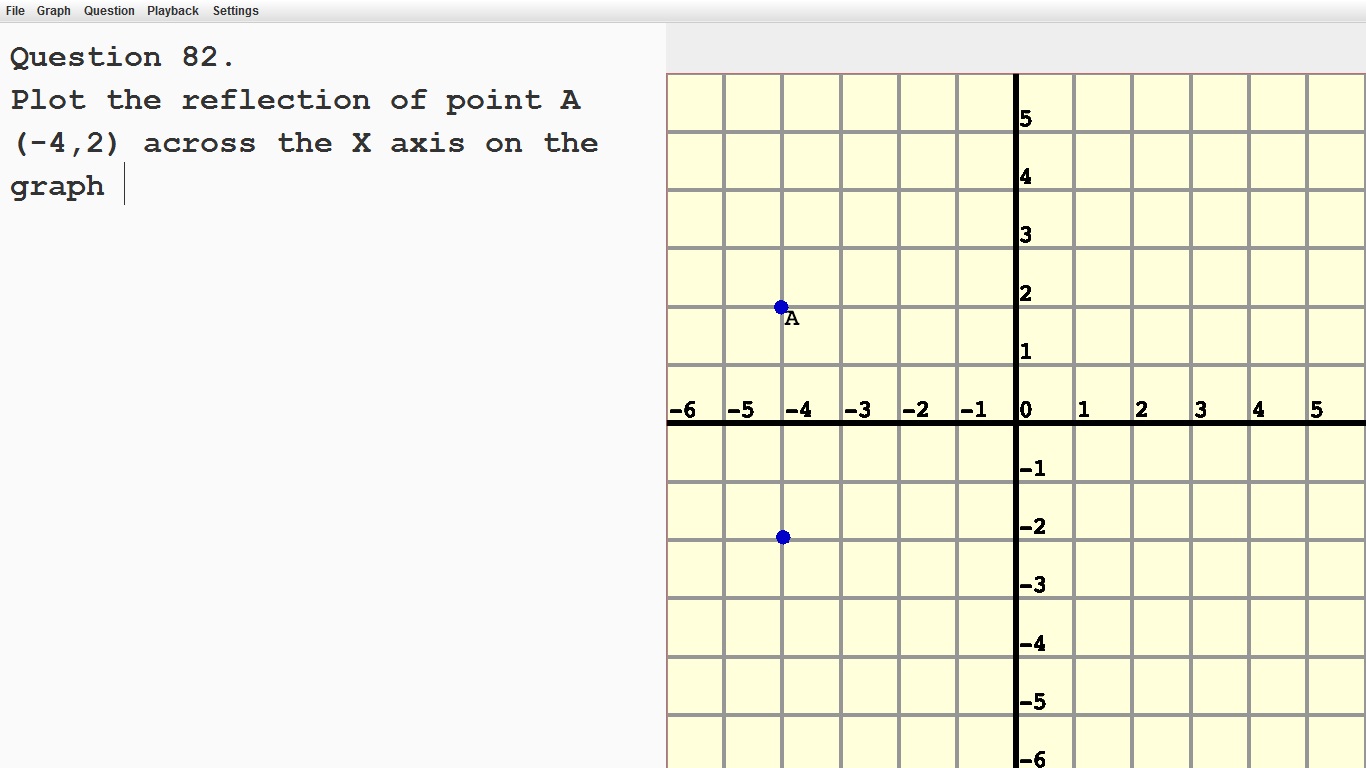
Recognize that when two ordered pairs differe only by signs, the locations of the points are related by reflections across one or both axes.
 |
 |
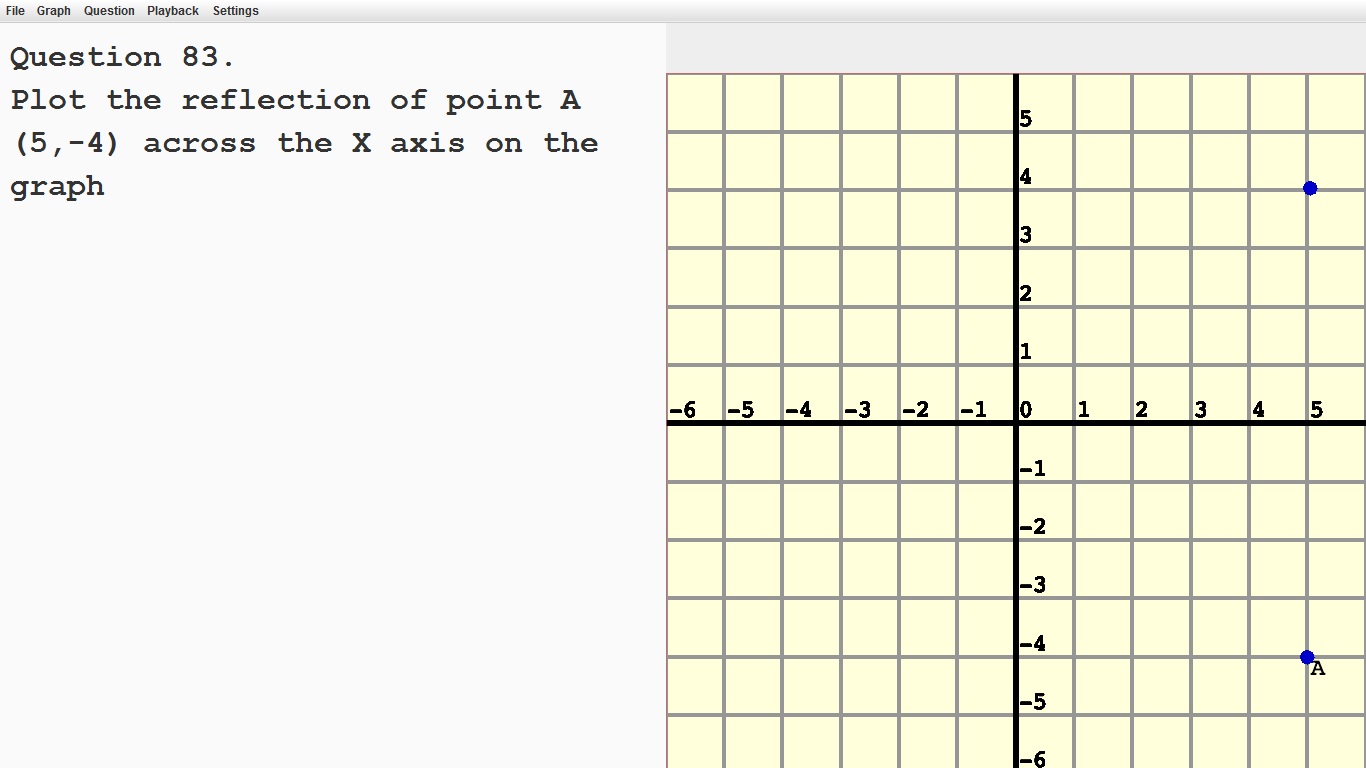 |
Find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane.
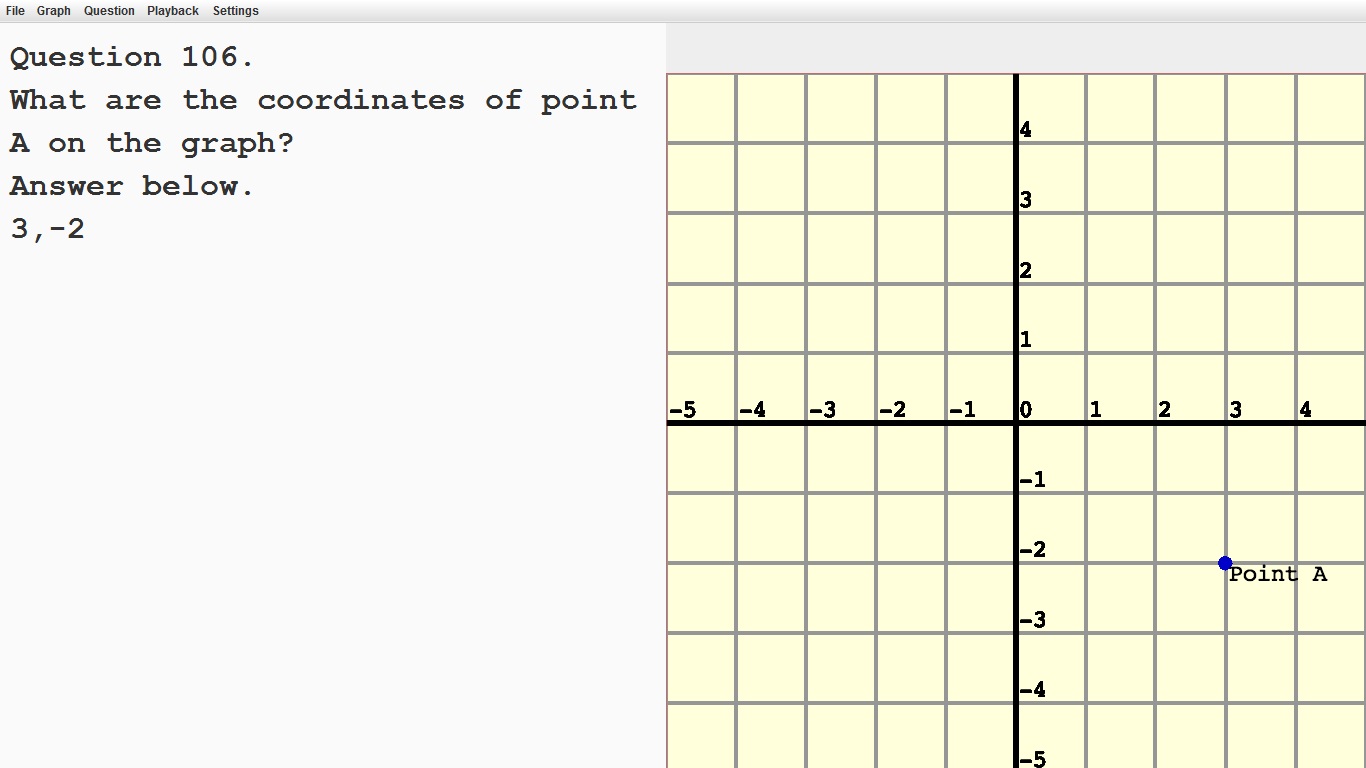 |
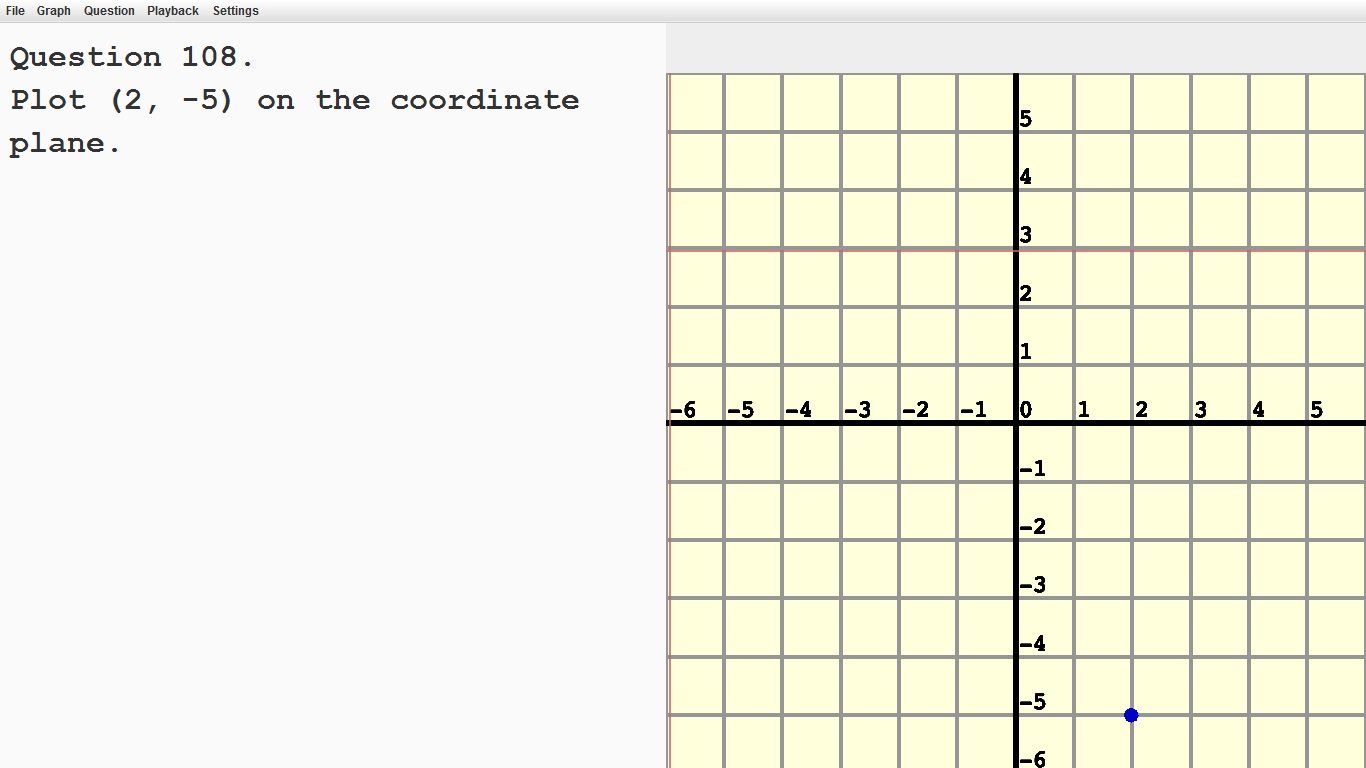 |
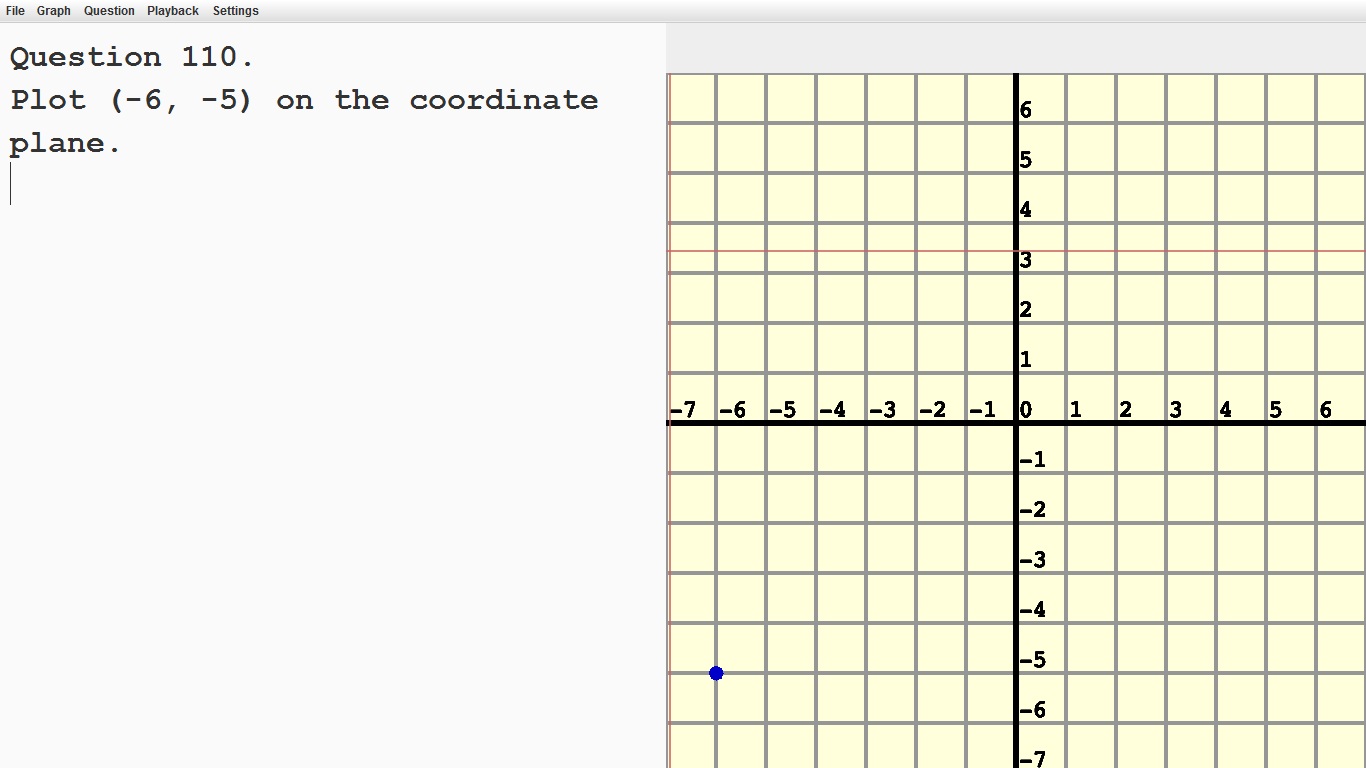 |